0x00 回顾
在开始阅读后续逻辑之前,我们回顾 signature 相关知识:
- 程序启动后,Suricata 去翻配置文件,按行读入
Signature,把Signature注册到DetectEngine中。 DetectEngineCtx内有一个sig_list链表,维护了所有的Signature,在读入完规则文件之后会排序,然后调用SigGroupBuild()构建匹配结构。Signature有几个重要字段:msg、alproto等规则中指定的属性;init_data里面有*smlists,其中有七个 SigMatch 链表;proto是一个 bitmap,表示 IP 报文中的“协议”字段,例如对于 UDP 规则,bit 17 设为 1。
前一篇文章阅读完了“读入 Signature 文件”逻辑。Suricata 在收到流量之后,显然不会逐条 Signature 去暴力匹配,应该存在相应的加速机制。因此,本文将聚焦于 SigGroupBuild() 过程。它是在 SigLoadSignatures() 过程中被调用的:
int SigLoadSignatures(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx, char *sig_file, int sig_file_exclusive)
{
// 初始化
if (!(sig_file != NULL && sig_file_exclusive == TRUE)) {
rule_files = ConfGetNode(varname);
if (rule_files != NULL) {
// 读入默认位置的规则文件
}
}
if (sig_file != NULL) {
// 读入命令行指定的规则文件
}
// 日志和错误处理
// 排序
SCSigRegisterSignatureOrderingFuncs(de_ctx);
SCSigOrderSignatures(de_ctx);
SCSigSignatureOrderingModuleCleanup(de_ctx);
// 这个函数是本文关注重点
/* Setup the signature group lookup structure and pattern matchers */
if (SigGroupBuild(de_ctx) < 0)
goto end;
// 返回
}本文编写过程中,大量使用了 LLM + RAG 辅助阅读源码。将源码的 .c 、.h 以及文档文件按 1000 长度切片之后向量化,获得了 26516 个向量。笔者使用的 LLM 是 Deepseek-V3,上下文长度 64k,故每次从数据库中取 100 个切片,与 prompt 一并输入给 LLM。每轮调用大约使用 32k 个 token,效果:
0x01 SigGroupBuild 概览
SigGroupBuild() 代码如下:
/**
* \brief Convert the signature list into the runtime match structure.
*
* \param de_ctx Pointer to the Detection Engine Context whose Signatures have
* to be processed
*
* \retval 0 On Success.
* \retval -1 On failure.
*/
int SigGroupBuild(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
Signature *s = de_ctx->sig_list;
// 遍历 sig_list 列表,给每个 sig 分配 id
de_ctx->signum = 0;
while (s != NULL) {
s->num = de_ctx->signum++;
s = s->next;
}
// 设置 FastPattern。以后 FP 是 FastPattern 的缩写
if (DetectSetFastPatternAndItsId(de_ctx) < 0)
return -1;
// 初始化 MPM Factory。MPM 是 Multi-Pattern Matching(多模式匹配)的缩写
SigInitStandardMpmFactoryContexts(de_ctx);
// 接下来是 4 个 SigAddressPrepare 相关
if (SigAddressPrepareStage1(de_ctx) != 0) {
FatalError("initializing the detection engine failed");
}
if (SigAddressPrepareStage2(de_ctx) != 0) {
FatalError("initializing the detection engine failed");
}
if (SigAddressPrepareStage3(de_ctx) != 0) {
FatalError("initializing the detection engine failed");
}
if (SigAddressPrepareStage4(de_ctx) != 0) {
FatalError("initializing the detection engine failed");
}
// 准备 Builtin、App、Pkt、Frame 四种 MPM
int r = DetectMpmPrepareBuiltinMpms(de_ctx);
r |= DetectMpmPrepareAppMpms(de_ctx);
r |= DetectMpmPreparePktMpms(de_ctx);
r |= DetectMpmPrepareFrameMpms(de_ctx);
if (r != 0) {
FatalError("initializing the detection engine failed");
}
// 准备 SigMatch
if (SigMatchPrepare(de_ctx) != 0) {
FatalError("initializing the detection engine failed");
}
ThresholdHashAllocate(de_ctx);
if (!DetectEngineMultiTenantEnabled()) {
VarNameStoreActivate();
}
return 0;
}接下来,我们跟进每一个函数,看看里面做了什么。
0x02 DetectSetFastPatternAndItsId
在看相关代码之前,我们先了解一下 fast pattern 概念。bot 提示我们看这篇文档。简而言之,由于逐个匹配 sig 会花费大量时间,Suricata 采用了“预过滤(prefilter)”机制,最常见的预过滤规则是 MPM(多模式串匹配)。只有在 MPM 阶段匹配成功的那些规则,才会去进一步验证是否命中。一个 sig 只有一个关键字会参与 MPM,默认情况下,Suricata 会按照长度等因素,自动选择一个关键字;而用户可以采用 fast_pattern 选项,强制指定一个关键字取代默认的那个。也有 MPM 以外的 prefilter,例如可以指定“TTL 字段等于某个值”作为 prefilter。
观察代码:
/**
* \brief Figure out the FP and their respective content ids for all the
* sigs in the engine.
*
* \param de_ctx Detection engine context.
*
* \retval 0 On success.
* \retval -1 On failure.
*/
int DetectSetFastPatternAndItsId(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
uint32_t cnt = 0;
for (Signature *s = de_ctx->sig_list; s != NULL; s = s->next) {
if (s->flags & SIG_FLAG_PREFILTER)
continue;
// 这个函数的作用:检查 sig 是否已经设置 mpm_sm(这个字段的类型是 SigMatch*)
// 若没有,则初始化一个
RetrieveFPForSig(de_ctx, s);
// 运行后获得 s->init_data->mpm_sm: {type:28, idx:0, ctx:0x00005555570eb090, next:null, prev:null}
if (s->init_data->mpm_sm != NULL) {
s->flags |= SIG_FLAG_PREFILTER;
cnt++;
}
}
/* no mpm rules */
if (cnt == 0)
return 0;
HashListTable *ht =
HashListTableInit(4096, PatternChopHashFunc, PatternChopCompareFunc, PatternFreeFunc);
BUG_ON(ht == NULL);
PatIntId max_id = 0;
for (Signature *s = de_ctx->sig_list; s != NULL; s = s->next) {
if (s->init_data->mpm_sm == NULL)
continue;
const int sm_list = s->init_data->mpm_sm_list;
BUG_ON(sm_list == -1);
// sm_list = 7
DetectContentData *cd = (DetectContentData *)s->init_data->mpm_sm->ctx;
// {content:"/cgi-bin/luci/;stok=/locale?form=country",
// content_len:40, replace_len:0, fp_chop_len:0,
// fp_chop_offset:0, flags:1114113, id:0, depth:0, offset:0,
// distance:0, within:0, spm_ctx:0x00005555570eb100, replace:0x0000000000000000}
DetectPatternTracker lookup = { .cd = cd, .sm_list = sm_list, .cnt = 0, .mpm = 0 };
DetectPatternTracker *res = HashListTableLookup(ht, &lookup, 0);
// 利用 hash 表去重
if (res) {
// 若 sig *s 所要求的匹配模式已经存在,则把 s->init_data->mpm_sm->ctx->id 设为已有的那条模式的 id
res->cnt++;
res->mpm += ((cd->flags & DETECT_CONTENT_MPM) != 0);
cd->id = res->cd->id;
SCLogDebug("%u: res id %u cnt %u", s->id, res->cd->id, res->cnt);
} else {
// 插入 hash 表
DetectPatternTracker *add = SCCalloc(1, sizeof(*add));
BUG_ON(add == NULL);
add->cd = cd;
add->sm_list = sm_list;
add->cnt = 1;
add->mpm = ((cd->flags & DETECT_CONTENT_MPM) != 0);
HashListTableAdd(ht, (void *)add, 0);
cd->id = max_id++;
SCLogDebug("%u: add id %u cnt %u", s->id, add->cd->id, add->cnt);
}
}
HashListTableFree(ht);
return 0;
}上述代码的功能就是对于每一个 sig,初始化 mpm_sm 这个 SigMatch。对于相同的匹配模式,则会合并成一个。
0x03 SigInitStandardMpmFactoryContexts
在 DetectSetFastPatternAndItsId() 之后,会调用 SigInitStandardMpmFactoryContexts()。观察代码:
static void SigInitStandardMpmFactoryContexts(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
DetectMpmInitializeBuiltinMpms(de_ctx);
}
void DetectMpmInitializeBuiltinMpms(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_proto_tcp_packet = SetupBuiltinMpm(de_ctx, "tcp-packet");
de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_stream = SetupBuiltinMpm(de_ctx, "tcp-stream");
de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_proto_udp_packet = SetupBuiltinMpm(de_ctx, "udp-packet");
de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_proto_other_packet = SetupBuiltinMpm(de_ctx, "other-ip");
}上面的代码为 tcp-packet, tcp-stream, udp-packet, other-ip 设置了内置 MPM。我们动态调试一番,看看 tcp-packet 的 MPM 是如何设置的:
static int32_t SetupBuiltinMpm(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx, const char *name)
{
/* default to whatever the global setting is */
int shared = (de_ctx->sgh_mpm_ctx_cnf == ENGINE_SGH_MPM_FACTORY_CONTEXT_SINGLE);
// shared = true
/* see if we use a unique or shared mpm ctx for this type */
int confshared = 0;
char confstring[256] = "detect.mpm.";
strlcat(confstring, name, sizeof(confstring));
strlcat(confstring, ".shared", sizeof(confstring));
// confstring = "detect.mpm.tcp-packet.shared"
if (ConfGetBool(confstring, &confshared) == 1)
shared = confshared;
int32_t ctx;
if (shared == 0) {
ctx = MPM_CTX_FACTORY_UNIQUE_CONTEXT;
SCLogDebug("using unique mpm ctx' for %s", name);
} else {
ctx = MpmFactoryRegisterMpmCtxProfile(de_ctx, name, DETECT_SM_LIST_PMATCH, ALPROTO_UNKNOWN);
// ctx = 152
SCLogDebug("using shared mpm ctx' for %s", name);
}
return ctx;
}代码中,首先查询了几个配置项,以决定使用独立或共享的 MPM context。根据文档,sgh_mpm_ctx_cnf 设为“full”表示每个 SigGroup 都有自己的 MPM ctx;“single”表示所有 SigGroup 共享一个 MPM ctx;默认设置为“auto”,表示算法 “ac” 使用单个 MPM ctx,其余算法同“full”情形。
跟进 MpmFactoryRegisterMpmCtxProfile() :
/**
* \brief Register a new Mpm Context.
*
* \param name A new profile to be registered to store this MpmCtx.
* \param sm_list sm_list for this name (might be variable with xforms)
* \param alproto app proto or ALPROTO_UNKNOWN if not for app-layer
*
* \retval id Return the id created for the new MpmCtx profile.
*/
int32_t MpmFactoryRegisterMpmCtxProfile(
DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx, const char *name, const int sm_list, const AppProto alproto)
{
// name="tcp-stream", sm_list=1, alproto=0(ALPROTO_UNKNOWN)
// 初次调用时,初始化 mpm_ctx_factory_container
// 我们现在并非第一次调用,container 中已经有 http_uri、http_raw_uri 等项目
if (de_ctx->mpm_ctx_factory_container == NULL) {
de_ctx->mpm_ctx_factory_container = SCCalloc(1, sizeof(MpmCtxFactoryContainer));
if (de_ctx->mpm_ctx_factory_container == NULL) {
FatalError("Error allocating memory");
}
de_ctx->mpm_ctx_factory_container->max_id = ENGINE_SGH_MPM_FACTORY_CONTEXT_START_ID_RANGE;
}
// 在已有的 mpm ctx 中寻找重复的,有则直接返回
MpmCtxFactoryItem *item = de_ctx->mpm_ctx_factory_container->items;
MpmCtxFactoryItem *pitem = NULL;
while (item) {
if (item->sm_list == sm_list && item->alproto == alproto && item->name != NULL &&
strcmp(item->name, name) == 0) {
return item->id;
}
pitem = item;
item = item->next;
}
// 新建 mpm ctx
MpmCtxFactoryItem *nitem = SCCalloc(1, sizeof(MpmCtxFactoryItem));
if (unlikely(nitem == NULL)) {
FatalError("Error allocating memory");
}
nitem->name = name;
nitem->sm_list = sm_list;
nitem->id = de_ctx->mpm_ctx_factory_container->max_id++;
nitem->alproto = alproto;
// 接下来,初始化负责 c->s 和 s->c 方向的 MpmCtx
/* toserver */
nitem->mpm_ctx_ts = SCCalloc(1, sizeof(MpmCtx));
if (nitem->mpm_ctx_ts == NULL) {
FatalError("Error allocating memory");
}
nitem->mpm_ctx_ts->flags |= MPMCTX_FLAGS_GLOBAL;
/* toclient */
nitem->mpm_ctx_tc = SCCalloc(1, sizeof(MpmCtx));
if (nitem->mpm_ctx_tc == NULL) {
FatalError("Error allocating memory");
}
nitem->mpm_ctx_tc->flags |= MPMCTX_FLAGS_GLOBAL;
// 把新建的 ctx 插入 de_ctx->mpm_ctx_factory_container->items 链表
/* store the newly created item */
if (pitem == NULL)
de_ctx->mpm_ctx_factory_container->items = nitem;
else
pitem->next = nitem;
de_ctx->mpm_ctx_factory_container->no_of_items++;
return nitem->id;
}这个函数会被调用四次,分别给 tcp-packet, tcp-stream, udp-packet, other-ip 创建 MPM ctx。运行完成之后,de_ctx.mpm_ctx_factory_container 的元素个数从 149 变成 153。
0x04 SigAddressPrepareStage1
紧跟着 SigInitStandardMpmFactoryContexts() 执行的,是四个 stage 的 SigAddressPrepare 过程。先来看 stage 1:
/**
* \brief Preprocess signature, classify ip-only, etc, build sig array
*
* \param de_ctx Pointer to the Detection Engine Context
*
* \retval 0 on success
* \retval -1 on failure
*/
int SigAddressPrepareStage1(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
uint32_t cnt_iponly = 0;
uint32_t cnt_payload = 0;
uint32_t cnt_applayer = 0;
uint32_t cnt_deonly = 0;
if (!(de_ctx->flags & DE_QUIET)) {
SCLogDebug("building signature grouping structure, stage 1: "
"preprocessing rules...");
}
// 按 sig 个数,分配 sig_array 空间
de_ctx->sig_array_len = DetectEngineGetMaxSigId(de_ctx);
de_ctx->sig_array_size = (de_ctx->sig_array_len * sizeof(Signature *));
de_ctx->sig_array = (Signature **)SCMalloc(de_ctx->sig_array_size);
if (de_ctx->sig_array == NULL)
goto error;
memset(de_ctx->sig_array,0,de_ctx->sig_array_size);
SCLogDebug("signature lookup array: %" PRIu32 " sigs, %" PRIu32 " bytes",
de_ctx->sig_array_len, de_ctx->sig_array_size);
/* now for every rule add the source group */
for (Signature *s = de_ctx->sig_list; s != NULL; s = s->next) {
// 把链表中的 sig 转存到数组
de_ctx->sig_array[s->num] = s;
SCLogDebug("Signature %" PRIu32 ", internal id %" PRIu32 ", ptrs %p %p ", s->id, s->num, s, de_ctx->sig_array[s->num]);
// 对于我们的规则,type=SIG_TYPE_APP_TX, flag 的 SIG_FLAG_APPLAYER 位为 1
// 更新计数器
if (s->type == SIG_TYPE_PDONLY) {
SCLogDebug("Signature %"PRIu32" is considered \"PD only\"", s->id);
} else if (s->type == SIG_TYPE_IPONLY) {
SCLogDebug("Signature %"PRIu32" is considered \"IP only\"", s->id);
cnt_iponly++;
} else if (SignatureIsInspectingPayload(de_ctx, s) == 1) {
SCLogDebug("Signature %"PRIu32" is considered \"Payload inspecting\"", s->id);
cnt_payload++;
} else if (s->type == SIG_TYPE_DEONLY) {
SCLogDebug("Signature %"PRIu32" is considered \"Decoder Event only\"", s->id);
cnt_deonly++;
} else if (s->flags & SIG_FLAG_APPLAYER) {
SCLogDebug("Signature %"PRIu32" is considered \"Applayer inspecting\"", s->id);
cnt_applayer++;
}
// 如果本条 sig 的 MPM 规则是负面规则,则设置 SIG_FLAG_MPM_NEG 位
if (RuleMpmIsNegated(s)) {
s->flags |= SIG_FLAG_MPM_NEG;
}
// 设置 s->mask。目前有效的 mask 位如下:
// SIG_MASK_REQUIRE_PAYLOAD, SIG_MASK_REQUIRE_FLOW, SIG_MASK_REQUIRE_FLAGS_INITDEINIT,
// SIG_MASK_REQUIRE_FLAGS_UNUSUAL, SIG_MASK_REQUIRE_NO_PAYLOAD,
// SIG_MASK_REQUIRE_DCERPC, SIG_MASK_REQUIRE_ENGINE_EVENT
// 举个例子,如果 SigMatch 要求匹配 SYN 包,则 SIG_MASK_REQUIRE_FLAGS_INITDEINIT 会被置 1
SignatureCreateMask(s);
// 传播 limit 条件。注释举了一个例子:
// alert tcp any any -> any any (msg:"Test Rule"; content:"1"; depth:1; content:"2"; distance:0; within:1; sid:1;)
// - 第一个 content 是 "1",并且设置了 depth:1,表示匹配的内容必须在数据包的前1个字节内
// - 第二个 content 是 "2",并且设置了 distance:0 和 within:1,表示匹配的内容必须紧跟在第一个 content 匹配的内容之后,并且在 1 个字节的范围内
// 于是,DetectContentPropagateLimits() 会把第二个 content 的 offset 设为 1,depth 设为 2
DetectContentPropagateLimits(s);
// 用 dsize 信息调整 depth
SigParseApplyDsizeToContent(s);
// 根据规则的端口、有否 MPM 等信息,设置 s->init_data->whitelist 数值
// 根据注释,这个值会影响 rule 分组
// A higher value leads to a higher likelihood of a rulegroup with this sig ending up as a contained group.
// 暂且看不懂 contained group 是什么意思
RuleSetWhitelist(s);
// 如果启用了 DETECT_PREFILTER_AUTO,则用下面的代码准备 prefilter
// 本次运行不涉及,默认是 DETECT_PREFILTER_MPM
/* if keyword engines are enabled in the config, handle them here */
if (de_ctx->prefilter_setting == DETECT_PREFILTER_AUTO &&
!(s->flags & SIG_FLAG_PREFILTER))
{
int prefilter_list = DETECT_TBLSIZE;
// TODO buffers?
/* get the keyword supporting prefilter with the lowest type */
for (int i = 0; i < DETECT_SM_LIST_MAX; i++) {
for (SigMatch *sm = s->init_data->smlists[i]; sm != NULL; sm = sm->next) {
if (sigmatch_table[sm->type].SupportsPrefilter != NULL) {
if (sigmatch_table[sm->type].SupportsPrefilter(s)) {
prefilter_list = MIN(prefilter_list, sm->type);
}
}
}
}
/* apply that keyword as prefilter */
if (prefilter_list != DETECT_TBLSIZE) {
for (int i = 0; i < DETECT_SM_LIST_MAX; i++) {
for (SigMatch *sm = s->init_data->smlists[i]; sm != NULL; sm = sm->next) {
if (sm->type == prefilter_list) {
s->init_data->prefilter_sm = sm;
s->flags |= SIG_FLAG_PREFILTER;
SCLogConfig("sid %u: prefilter is on \"%s\"", s->id, sigmatch_table[sm->type].name);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 给每个 smlist 运行 buffer 初始化逻辑
/* run buffer type callbacks if any */
for (int x = 0; x < DETECT_SM_LIST_MAX; x++) {
if (s->init_data->smlists[x])
DetectEngineBufferRunSetupCallback(de_ctx, x, s);
}
for (uint32_t x = 0; x < s->init_data->buffer_index; x++) {
DetectEngineBufferRunSetupCallback(de_ctx, s->init_data->buffers[x].id, s);
}
de_ctx->sig_cnt++;
}
if (!(de_ctx->flags & DE_QUIET)) {
SCLogInfo("%" PRIu32 " signatures processed. %" PRIu32 " are IP-only "
"rules, %" PRIu32 " are inspecting packet payload, %"PRIu32
" inspect application layer, %"PRIu32" are decoder event only",
de_ctx->sig_cnt, cnt_iponly, cnt_payload, cnt_applayer,
cnt_deonly);
SCLogConfig("building signature grouping structure, stage 1: "
"preprocessing rules... complete");
}
if (DetectFlowbitsAnalyze(de_ctx) != 0)
goto error;
return 0;
error:
return -1;
}总结一句:SigAddressPrepareStage1() 的作用是把 signature 链表转存到数组中;对于每个 signature,用已知信息尽量填写各种限制条件;在启用 DETECT_PREFILTER_AUTO 的情况下初始化一些 prefilter;运行 buffer 初始化的 callback 函数。
0x05 SigAddressPrepareStage2
stage2 代码如下:
/**
* \brief Fill the global src group head, with the sigs included
*
* \param de_ctx Pointer to the Detection Engine Context whose Signatures have
* to be processed
*
* \retval 0 On success
* \retval -1 On failure
*/
int SigAddressPrepareStage2(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
SCLogDebug("building signature grouping structure, stage 2: "
"building source address lists...");
// 给 ipv4、ipv6 的 RadixTree 分配空间
IPOnlyInit(de_ctx, &de_ctx->io_ctx);
// c->s、s->c 的 tcp、udp 规则组
// CVE-2023-1389 的那条规则即是在此进入了规则组
de_ctx->flow_gh[1].tcp = RulesGroupByPorts(de_ctx, IPPROTO_TCP, SIG_FLAG_TOSERVER);
de_ctx->flow_gh[0].tcp = RulesGroupByPorts(de_ctx, IPPROTO_TCP, SIG_FLAG_TOCLIENT);
de_ctx->flow_gh[1].udp = RulesGroupByPorts(de_ctx, IPPROTO_UDP, SIG_FLAG_TOSERVER);
de_ctx->flow_gh[0].udp = RulesGroupByPorts(de_ctx, IPPROTO_UDP, SIG_FLAG_TOCLIENT);
// IP proto 规则组
/* Setup the other IP Protocols (so not TCP/UDP) */
RulesGroupByProto(de_ctx);
// 处理 IPONLY 和 DEONLY 规则
/* now for every rule add the source group to our temp lists */
for (Signature *s = de_ctx->sig_list; s != NULL; s = s->next) {
SCLogDebug("s->id %"PRIu32, s->id);
if (s->type == SIG_TYPE_IPONLY) {
IPOnlyAddSignature(de_ctx, &de_ctx->io_ctx, s);
} else if (s->type == SIG_TYPE_DEONLY) {
DetectEngineAddDecoderEventSig(de_ctx, s);
}
}
// 构建 RadixTree
IPOnlyPrepare(de_ctx);
// 下面这个函数是空的
IPOnlyPrint(de_ctx, &de_ctx->io_ctx);
return 0;
}DEONLY 是“Decoder Event Only”的缩写,匹配解码器产生的事件而非具体内容。
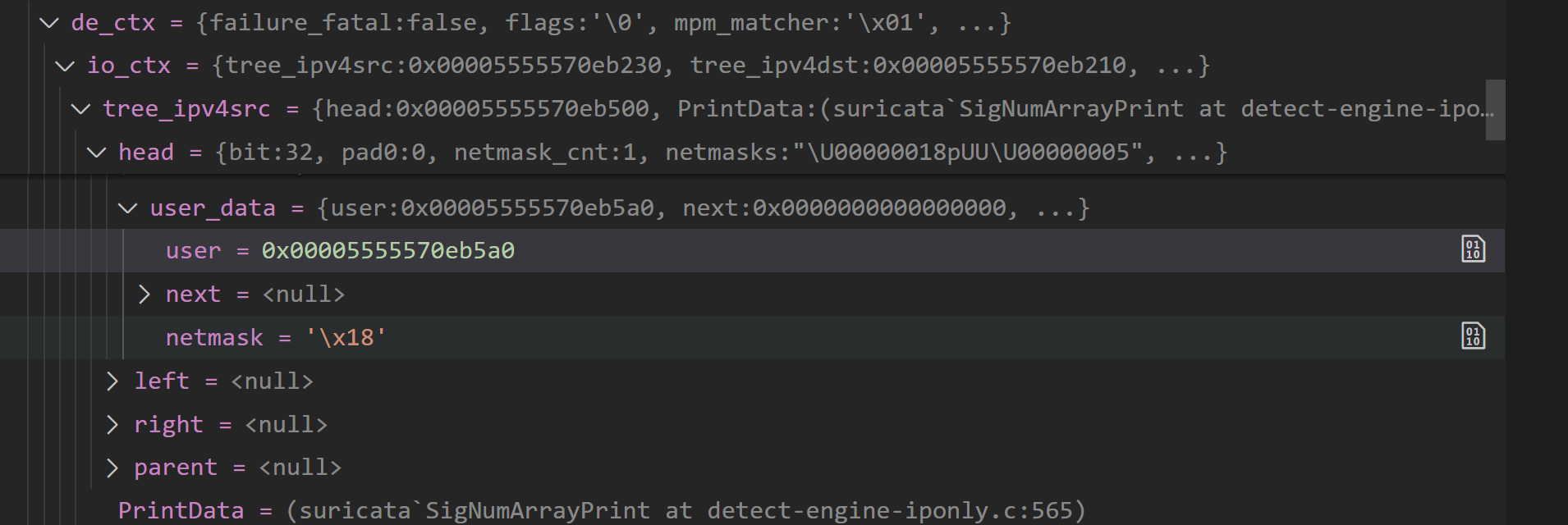
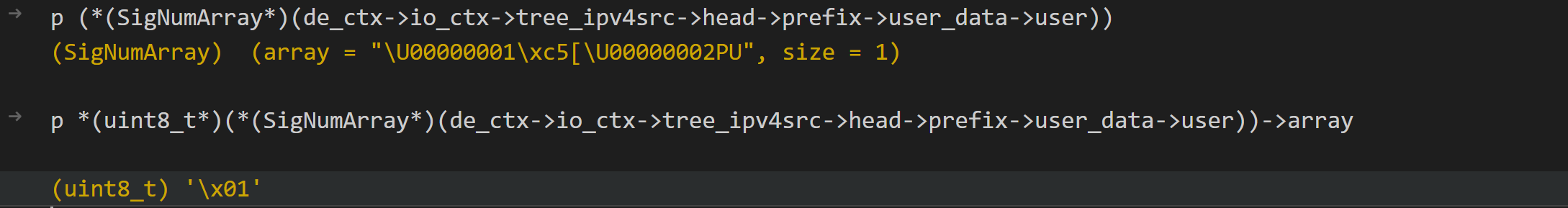
我们详细讨论一下 RadixTree。一个 de_ctx 中存在四个 RadixTree,即 ipv4src、ipv4dst、ipv6src、ipv6dst。它们由 IPOnlyInit() 分配空间,在 IPOnlyPrepare() 中构建。
SCRadixTree 由 SCRadixNode 构成,一个 SCRadixNode 可以包含一个 SCRadixPrefix 指针,而 SCRadixPrefix 中维护了一个 SCRadixUserData 链表。在上面的代码执行完毕后,RadixTree 中的 user data 会存放 SigNumArrays。
因此,Stage 2 过程做的事情就是:构建 ip 地址的 RadixTree,以及 port group、proto group。
不过,我们使用的那条 CVE-2023-1389 规则并不是 IPONLY 的,所以没有体现在 Stage 2 工作过程中。我们换一条规则:
alert tcp 192.168.25.0/24 any -> 192.168.25.21 8000 (msg:"attack!"; sid:1000002; rev:1;)这条规则仅靠 IP 层报文就可以判断,所以类型是 SIG_TYPE_IPONLY。可以观察到 ipv4src、ipv4dst 的 RadixTree:
0x06 SigAddressPrepareStage3
继续看 stage 3。
int SigAddressPrepareStage3(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
/* prepare the decoder event sgh */
DetectEngineBuildDecoderEventSgh(de_ctx);
return 0;
}
static void DetectEngineBuildDecoderEventSgh(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
if (de_ctx->decoder_event_sgh == NULL)
return;
uint32_t max_idx = DetectEngineGetMaxSigId(de_ctx);
SigGroupHeadSetSigCnt(de_ctx->decoder_event_sgh, max_idx);
SigGroupHeadBuildMatchArray(de_ctx, de_ctx->decoder_event_sgh, max_idx);
}
void SigGroupHeadSetSigCnt(SigGroupHead *sgh, uint32_t max_idx)
{
// 把 sgh->init->sig_cnt 设为 sgh 内的 sig 数量
#ifdef HAVE_POPCNT64
// 如果有 popcnt 指令,则使用加速版的实现
sgh->init->sig_cnt = Popcnt(sgh->init->sig_array, sgh->init->sig_size);
#else
// 暴力给 sgh->init->sig_array 这个 bitmap 计数
uint32_t cnt = 0;
for (uint32_t sig = 0; sig < max_idx + 1; sig++) {
if (sgh->init->sig_array[sig / 8] & (1 << (sig % 8)))
cnt++;
}
sgh->init->sig_cnt = cnt;
#endif
return;
}
int SigGroupHeadBuildMatchArray(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx, SigGroupHead *sgh,
uint32_t max_idx)
{
// 构建 sgh->init->match_array 指针数组,指向本 SigGroup 包含的 Signature
Signature *s = NULL;
uint32_t idx = 0;
uint32_t sig = 0;
if (sgh == NULL)
return 0;
BUG_ON(sgh->init->match_array != NULL);
sgh->init->match_array = SCMalloc(sgh->init->sig_cnt * sizeof(Signature *));
if (sgh->init->match_array == NULL)
return -1;
memset(sgh->init->match_array, 0, sgh->init->sig_cnt * sizeof(Signature *));
for (sig = 0; sig < max_idx + 1; sig++) {
if (!(sgh->init->sig_array[(sig / 8)] & (1 << (sig % 8))) )
continue;
s = de_ctx->sig_array[sig];
if (s == NULL)
continue;
sgh->init->match_array[idx] = s;
idx++;
}
return 0;
}stage 3 比前两个 stage 更简单。针对 decoder event only 类型的规则,有一个专门的 SigGroup,其 head 是 de_ctx->decoder_event_sgh。本 stage 通过其 bitmap,计算其 sig 数量,并构建指针数组 match_array,指向这些 sig。
sig_array:分别是 de_ctx->sig_array 和 sgh->init->sig_array。前者是 sig_list 链表的转储,保存了所有规则;后者是一个 bitmap,第 k 位对应第 k 条规则。上述代码中的 DetectEngineBuildDecoderEventSgh() 和 SigGroupHeadBuildMatchArray() 之实现,是通用逻辑。stage 2 的 RulesGroupByProto() 和 RulesGroupByPorts() 也调用了它们。
0x07 SigAddressPrepareStage4
现在,来看 SigAddressPrepare 系列的最后一个 stage:
int SigAddressPrepareStage4(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
SCEnter();
//SCLogInfo("sgh's %"PRIu32, de_ctx->sgh_array_cnt);
uint32_t cnt = 0;
for (uint32_t idx = 0; idx < de_ctx->sgh_array_cnt; idx++) {
// 考虑每个 SigGroup
SigGroupHead *sgh = de_ctx->sgh_array[idx];
if (sgh == NULL)
continue;
SCLogDebug("sgh %p", sgh);
// 在 HAVE_MAGIC 的情况下,若本 SigGroup 内有一条 sig 的 file_flags 包含 FILE_SIG_NEED_MAGIC,
// 则给 sgh->flags 设置 SIG_GROUP_HEAD_HAVEFILEMAGIC
SigGroupHeadSetFilemagicFlag(de_ctx, sgh);
// 处理 FileHash 相关的 flag,考虑 MD5、SHA1、SHA256
// 例如,若有 sig 的 file_flags 包含 FILE_SIG_NEED_MD5,则给 SigGroup 设置 SIG_GROUP_HEAD_HAVEFILEMD5
SigGroupHeadSetFileHashFlag(de_ctx, sgh);
// 若有 sig 要匹配文件大小,则给 SigGroup 设置 SIG_GROUP_HEAD_HAVEFILESIZE
SigGroupHeadSetFilesizeFlag(de_ctx, sgh);
// 填写 sgh->filestore_cnt 计数器,即有 SIG_FLAG_FILESTORE 这个 flag 的 sig 数量
SigGroupHeadSetFilestoreCount(de_ctx, sgh);
SCLogDebug("filestore count %u", sgh->filestore_cnt);
// 一个很复杂的函数,为 SigGroup 设置预过滤器引擎
PrefilterSetupRuleGroup(de_ctx, sgh);
// 构建 sgh->non_pf_syn_store_array 和 sgh->non_pf_other_store_array
// 保存没有预过滤器的 sig 的 id、mask、alproto
SigGroupHeadBuildNonPrefilterArray(de_ctx, sgh);
sgh->id = idx;
cnt++;
}
SCLogPerf("Unique rule groups: %u", cnt);
// 报告 MPM 相关的一些统计信息
MpmStoreReportStats(de_ctx);
if (de_ctx->decoder_event_sgh != NULL) {
/* no need to set filestore count here as that would make a
* signature not decode event only. */
SigGroupHeadBuildNonPrefilterArray(de_ctx, de_ctx->decoder_event_sgh);
}
// 以下是把分组结果 dump 到硬盘的相关代码
int dump_grouping = 0;
(void)ConfGetBool("detect.profiling.grouping.dump-to-disk", &dump_grouping);
if (dump_grouping) {
int add_rules = 0;
(void)ConfGetBool("detect.profiling.grouping.include-rules", &add_rules);
int add_mpm_stats = 0;
(void)ConfGetBool("detect.profiling.grouping.include-mpm-stats", &add_mpm_stats);
RulesDumpGrouping(de_ctx, add_rules, add_mpm_stats);
}
for (uint32_t idx = 0; idx < de_ctx->sgh_array_cnt; idx++) {
SigGroupHead *sgh = de_ctx->sgh_array[idx];
if (sgh == NULL)
continue;
SigGroupHeadInitDataFree(sgh->init);
sgh->init = NULL;
}
/* cleanup the hashes now since we won't need them
* after the initialization phase. */
SigGroupHeadHashFree(de_ctx);
SCReturnInt(0);
}本阶段的主要工作是,对于每个 SigGroup,用其中包含的那些 sig 的 flag,设置 SigGroup 的 flag,例如“是否有关注文件 SHA1 的规则”。另外,为本 SigGroup 配置预过滤器。
0x08 DetectMpmPrepare
stage4 之后的过程是 DetectMpmPrepare。它分为四个步骤:
int r = DetectMpmPrepareBuiltinMpms(de_ctx);
r |= DetectMpmPrepareAppMpms(de_ctx);
r |= DetectMpmPreparePktMpms(de_ctx);
r |= DetectMpmPrepareFrameMpms(de_ctx);
if (r != 0) {
FatalError("initializing the detection engine failed");
}
依次观察。
/**
* \brief initialize mpm contexts for builtin buffers that are in
* "single or "shared" mode.
*/
int DetectMpmPrepareBuiltinMpms(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
int r = 0;
MpmCtx *mpm_ctx = NULL;
if (de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_proto_tcp_packet != MPM_CTX_FACTORY_UNIQUE_CONTEXT) {
mpm_ctx = MpmFactoryGetMpmCtxForProfile(de_ctx, de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_proto_tcp_packet, 0);
if (mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare != NULL) {
r |= mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare(mpm_ctx);
}
mpm_ctx = MpmFactoryGetMpmCtxForProfile(de_ctx, de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_proto_tcp_packet, 1);
if (mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare != NULL) {
r |= mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare(mpm_ctx);
}
}
if (de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_proto_udp_packet != MPM_CTX_FACTORY_UNIQUE_CONTEXT) {
mpm_ctx = MpmFactoryGetMpmCtxForProfile(de_ctx, de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_proto_udp_packet, 0);
if (mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare != NULL) {
r |= mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare(mpm_ctx);
}
mpm_ctx = MpmFactoryGetMpmCtxForProfile(de_ctx, de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_proto_udp_packet, 1);
if (mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare != NULL) {
r |= mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare(mpm_ctx);
}
}
if (de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_proto_other_packet != MPM_CTX_FACTORY_UNIQUE_CONTEXT) {
mpm_ctx = MpmFactoryGetMpmCtxForProfile(de_ctx, de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_proto_other_packet, 0);
if (mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare != NULL) {
r |= mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare(mpm_ctx);
}
}
if (de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_stream != MPM_CTX_FACTORY_UNIQUE_CONTEXT) {
mpm_ctx = MpmFactoryGetMpmCtxForProfile(de_ctx, de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_stream, 0);
if (mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare != NULL) {
r |= mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare(mpm_ctx);
}
mpm_ctx = MpmFactoryGetMpmCtxForProfile(de_ctx, de_ctx->sgh_mpm_context_stream, 1);
if (mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare != NULL) {
r |= mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare(mpm_ctx);
}
}
return r;
}此函数是用于初始化几个内置 MPM 的,包括: tcp_packet 、 udp_packet 、 other_packet 、 stream。
/**
* \brief initialize mpm contexts for applayer buffers that are in
* "single or "shared" mode.
*/
int DetectMpmPrepareAppMpms(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
int r = 0;
// 初始化 app_mpms_list 中的每一个 MPM
const DetectBufferMpmRegistry *am = de_ctx->app_mpms_list;
while (am != NULL) {
int dir = (am->direction == SIG_FLAG_TOSERVER) ? 1 : 0;
if (am->sgh_mpm_context != MPM_CTX_FACTORY_UNIQUE_CONTEXT)
{
MpmCtx *mpm_ctx = MpmFactoryGetMpmCtxForProfile(de_ctx, am->sgh_mpm_context, dir);
if (mpm_ctx != NULL) {
if (mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare != NULL) {
r |= mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare(mpm_ctx);
}
}
}
am = am->next;
}
return r;
}上述代码给 de_ctx->app_mpms_list 中的每一个 MPM 做了初始化。在动态调试中,这些 MPM 包括 http_uri 、 http_raw_uri 、 http_request_line 等。
/**
* \brief initialize mpm contexts for applayer buffers that are in
* "single or "shared" mode.
*/
int DetectMpmPreparePktMpms(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
SCLogDebug("preparing pkt mpm");
int r = 0;
// 初始化 pkt_mpms_list 中的 MPM
const DetectBufferMpmRegistry *am = de_ctx->pkt_mpms_list;
while (am != NULL) {
SCLogDebug("%s", am->name);
if (am->sgh_mpm_context != MPM_CTX_FACTORY_UNIQUE_CONTEXT)
{
MpmCtx *mpm_ctx = MpmFactoryGetMpmCtxForProfile(de_ctx, am->sgh_mpm_context, 0);
if (mpm_ctx != NULL) {
if (mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare != NULL) {
r |= mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare(mpm_ctx);
SCLogDebug("%s: %d", am->name, r);
}
}
}
am = am->next;
}
return r;
}这份代码与 DetectMpmPrepareAppMpms() 非常相似,它初始化 de_ctx->pkt_mpms_list 中的 MPM。动态调试时,这个列表包含 icmpv4.hdr 、tcp.hdr、udp.hdr、 icmpv6.hdr 等 MPM。
/**
* \brief initialize mpm contexts for applayer buffers that are in
* "single or "shared" mode.
*/
int DetectMpmPrepareFrameMpms(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
SCLogDebug("preparing frame mpm");
int r = 0;
const DetectBufferMpmRegistry *am = de_ctx->frame_mpms_list;
while (am != NULL) {
SCLogDebug("am %p %s sgh_mpm_context %d", am, am->name, am->sgh_mpm_context);
SCLogDebug("%s", am->name);
if (am->sgh_mpm_context != MPM_CTX_FACTORY_UNIQUE_CONTEXT) {
int dir = (am->direction == SIG_FLAG_TOSERVER) ? 1 : 0;
MpmCtx *mpm_ctx = MpmFactoryGetMpmCtxForProfile(de_ctx, am->sgh_mpm_context, dir);
SCLogDebug("%s: %d mpm_Ctx %p", am->name, r, mpm_ctx);
if (mpm_ctx != NULL) {
if (mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare != NULL) {
r |= mpm_table[de_ctx->mpm_matcher].Prepare(mpm_ctx);
SCLogDebug("%s: %d", am->name, r);
}
}
}
am = am->next;
}
return r;
}上述代码初始化了 de_ctx->frame_mpms_list 中的 MPM。动态调试时,这个链表是空的。
0x09 SigMatchPrepare
SigMatchPrepare() 是 SigGroupBuild 的最后一项主要过程。代码如下:
/** \internal
* \brief perform final per signature setup tasks
*
* - Create SigMatchData arrays from the init only SigMatch lists
* - Setup per signature inspect engines
* - remove signature init data.
*/
static int SigMatchPrepare(DetectEngineCtx *de_ctx)
{
SCEnter();
Signature *s = de_ctx->sig_list;
for (; s != NULL; s = s->next) {
// 遍历所有 signature
// 给 s 添加 frame、packet、app 检测引擎
// 引擎会被生成并添加到 s->frame_inspect、s->pkt_inspect、s->app_inspect
DetectEngineAppInspectionEngine2Signature(de_ctx, s);
// smlists 转存到数组 sm_arrays
for (int type = 0; type < DETECT_SM_LIST_MAX; type++) {
/* skip PMATCH if it is used in a stream 'app engine' instead */
if (type == DETECT_SM_LIST_PMATCH && (s->init_data->init_flags & SIG_FLAG_INIT_STATE_MATCH))
continue;
SigMatch *sm = s->init_data->smlists[type];
s->sm_arrays[type] = SigMatchList2DataArray(sm);
}
// 给 s->pkt_inspect 添加 PayloadMatches 和 PacketMatches
DetectEnginePktInspectionSetup(s);
if (rule_engine_analysis_set) {
EngineAnalysisAddAllRulePatterns(de_ctx, s);
EngineAnalysisRules2(de_ctx, s);
}
// 释放 smlists 链表空间
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < DETECT_SM_LIST_MAX; i++) {
SigMatch *sm = s->init_data->smlists[i];
while (sm != NULL) {
SigMatch *nsm = sm->next;
SigMatchFree(de_ctx, sm);
sm = nsm;
}
}
// 对 sigmatch_table[transform] 执行各自的 Free 函数
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < (uint32_t)s->init_data->transforms.cnt; i++) {
if (s->init_data->transforms.transforms[i].options) {
int transform = s->init_data->transforms.transforms[i].transform;
sigmatch_table[transform].Free(
de_ctx, s->init_data->transforms.transforms[i].options);
s->init_data->transforms.transforms[i].options = NULL;
}
}
// 释放 SignatureInitDataBuffer
for (uint32_t x = 0; x < s->init_data->buffer_index; x++) {
SigMatch *sm = s->init_data->buffers[x].head;
while (sm != NULL) {
SigMatch *nsm = sm->next;
SigMatchFree(de_ctx, sm);
sm = nsm;
}
}
// 释放 s->init_data
SCFree(s->init_data->buffers);
SCFree(s->init_data);
s->init_data = NULL;
}
DumpPatterns(de_ctx);
SCReturnInt(0);
}这份代码首先构建了 s->frame_inspect、 s->pkt_inspect 、 s->app_inspect 这三个检测引擎链表,然后把 smlists 链表转存成数组。现在 s->init_data 的任务已经完成,将它的空间释放掉。
0x0a 总结
读入所有规则之后,函数 SigGroupBuild() 负责构建规则组。其中发生了如下过程:
- 给每个 sig 分配“内部 id”。这个 id 从 0 开始分配,与用户在规则文件中提供的
sid参数不同。之后会有一些 bitmap 与这个内部 id 相关。 - 给每个 sig 设置 MPM SigMatch。
- SigAddressPrepareStage1,把原先用链表存储的 sig 转存到数组,并利用已知信息,尽量填写
depth等限制条件。 - SigAddressPrepareStage2,构建端口规则组、IP proto 规则组,构建 IP 地址的 RadixTree。
- SigAddressPrepareStage3,构建 decoder event only 的规则组。
- SigAddressPrepareStage4,对每个规则组,设置其 flag,并配置规则组的预过滤器。
- 初始化所有 MPM。
- 对每个 sig,构建
s->frame_inspect、s->pkt_inspect、s->app_inspect这三个检测引擎链表,把 smlists 链表转存为数组,释放init_data。

